| ultramarin marine translations |
| ultramarin.online | ||||
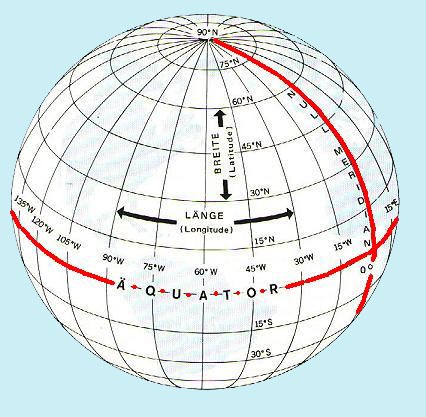
| geografische breedte breedte(graad) |
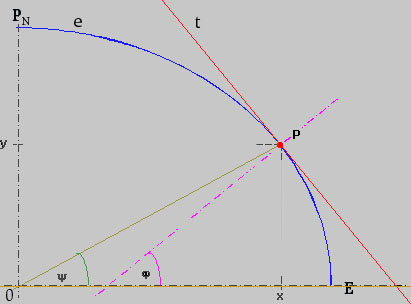
hoek die de normale door het waargenomen punt op het referentievlak (bv. de aardbol) vormt met het equatoriale vlak, poolwaarts van 00° tot 90° voor het noordelijk halfrond voorzien van N of plus teken, voor het zuidelijk halfrond voorzien van Z of minus teken.. | |||
| (geographische) Breite Breitengrad |
Winkel, den die Normale durch den betrachteten Punkt auf der Bezugsfläche (z. B. Erdkugel) mit der Äquatorebene bildet, polwärts von 00° bis 90°, für die Nordhalbkugel mit dem Zusatzzeichen N oder mit Vorzeichen plus, für die Südhalbkugel mit dem Zusatzzeichen S oder mit Vorzeichen minus gezählt | |||
| (geographic) latitude degree of latitude parallel |
the angular distance from a primary
great circle or plane. terrestrial latitude: the angular distance from the equator, measured northward or southward through 90° and labeled N or S to indicate the direction of measurement; astronomical latitude at a station: the angular distance between the plumb line and the plane of the celestial equator; geodetic or topographical latitude at a station: the angular distance between the plane of the geodetic equator and a normal to the ellipsoid; geocentric latitude: the angle at the center of the reference ellipsoid between the celestial equator and a radius vector to a point on the ellipsoid; assumed (or chosen) latitude: the latitude at which an observer is assumed to be located for an observation or computation; observed latitude: latitude determined by one or more lines of position extending in a generally east-west direction; fictitious latitude: the angular distance from a fictitious equator; grid latitude: the angular distance from a grid equator; transverse or inverse latitude: the angular distance from a transverse equator; oblique latitude: the angular distance from an oblique equator; middle (mid) latitude: the latitude at which the arc length of the parallel separating the meridians passing through two specific points is exactly equal to the departure in proceeding from one point to the other by middle-latitude sailing; mean latitude: half the arithmetical sum of the latitude of two places on the same side of the equator; usually used in middle-latitude sailing for want of a practical means of determining middle latitude; difference of latitude: is the shorter arc of any meridian between the parallels of two places, expressed in angular measure; magnetic latitude (magnetic inclination, magnetic dip): the angular distance between the horizontal and the direction of a line of force of the earth's magnetic field at any point; geomagnetic latitude: the angular distance from the geomagnetic equator: parallel of latitude: a circle (or approximation of a circle) of the earth, parallel to the equator, and connecting points of equal latitude- or a circle of the celestial sphere, parallel to the ecliptic. celestial latitude: the angular distance north or south of the ecliptic. Geodetic and sometimes astronomical latitude are also called geographic latitude. Geodetic latitude is used for charts. |
|||
| latitude géographique (degré de) latitude |
||||
| (grado de) latitud | ||||
| latitudine parallelo |
||||
| bredde(grad) | ||||
| latitud | ||||